Healthcare monitoring system are used to streamline the medical claims process, which eases the relationship between provider and government and efficiently speeds up the patient’s treatment lifecycle. These solutions leverage automation attributes so hospitals and clinics can settle or stop any limitations that can potentially disrupt the claims processing and billing workflow. The health schemes aim at establishing a suitable on-line Management Information
System and Decision Support System for the Plan Scheme of the Government. The system is envisaged to track the fund disbursement from the Government up to the last beneficiary under plan schemes and ultimately report utilization under these schemes at different levels of implementation on a real time basis. The importance or need for a claim and assurance management system is having a common platform which can provide details of Ministry wise, Scheme-wise, State-wise and Agency-wise sanction issued and releases made both through the Treasury route and the Special Purpose Vehicle route.
The latest global monitoring reports on universal health coverage (UHC) and financial protection in health, published by WHO and the World Bank, identified mixed trends before the COVID-19 pandemic. Health service coverage enhanced steadily from an index of 45 in 2000 to 67 in 2019, while the ratio of the population is a key message with out-of-pocket health spending surpassing 10% of their household budget from 9.4% in 2000 to 13.2% in 2017.
Universal health coverage (UHC) is the goal of ensuring that all people have access to the full range of quality health services they need, without facing financial hardship. UHC is one of the targets of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), which are a set of 17 global goals adopted by the United Nations in 2015 to finish poverty, save the planet, and provide peace and prosperity for all by 2030. UHC is part of SDG 3, which aims to "ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages.
Overall, urgent actions are needed to achieve the target of having an additional one billion people enjoying UHC by 2030. Based on current trends, approximately 730 million people will miss out on UHC; if the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic and its disruptions are taken into account, that shortfall could rise to 840 million.
Challenges
Administering health insurance schemes can be a complex and challenging task, given the diverse population, geographic spread, and varying levels of health awareness and literacy. The Indian healthcare system is a mix of public and private providers, and insurance schemes are an essential part of the system to provide financial protection and access to healthcare services.
The challenges are-
-
Lack of Awareness: One of the primary challenges in administering health insurance schemes is a lack of understanding of insurance products among the population, the types of policies available, and selecting the right one for their needs.
-
Cost of Healthcare Services: This is rapidly increasing due to rising demand, technological advancements, and an aging population. This has led to an increase in the cost of health insurance premiums, which results to opt for policies with limited coverage that may not provide adequate financial protection in case of a medical emergency.
-
Fraud and Abuse: There have been instances of providers charging exorbitant fees for medical procedures, over-prescribing medicines, and inflating bills, leading to a rise in insurance claims. This has led to insurance companies becoming more stringent in their policy provisions, resulting in the denial of genuine claims, and creating dissatisfaction among policyholders.
-
Implementation and Management: The lack of a centralized system for data collection, claims processing, and grievance redressal leads to inefficiencies, delays, and inconsistencies in the administration of insurance schemes. The underfunding of government-sponsored schemes, inadequate infrastructure, and shortage of trained personnel pose significant challenges in delivering quality healthcare services to the insured population.
To overcome these challenges and accelerate progress towards UHC, WHO recommends reorienting health systems to primary health care (PHC), which is a people-centered approach that integrates health services at the community level and addresses the social determinants of health. PHC can deliver most (90%) of essential UHC interventions and achieve 75% of projected health gains from the SDGs. PHC also requires strong governance, adequate financing, a skilled workforce, quality-assured products, and effective information systems.
Need of Health Schemes
- The health schemes offer the best health services to every age group and gender.
- The policy focuses on providing universal access to excellent quality healthcare services at a reasonable cost.
- Offering access to better treatment, lowering expenses related to health care services, and improving quality.
- It aims to reduce premature mortality from cancer, cardiovascular diseases, chronic respiratory diseases, and diabetes by 25% by 2025.
- This policy recognizes the importance of sustainable development and time-bound quantitative goals.
- All the health policies in India improve overall health status through promotional, palliative, and rehabilitative services.
Features
-
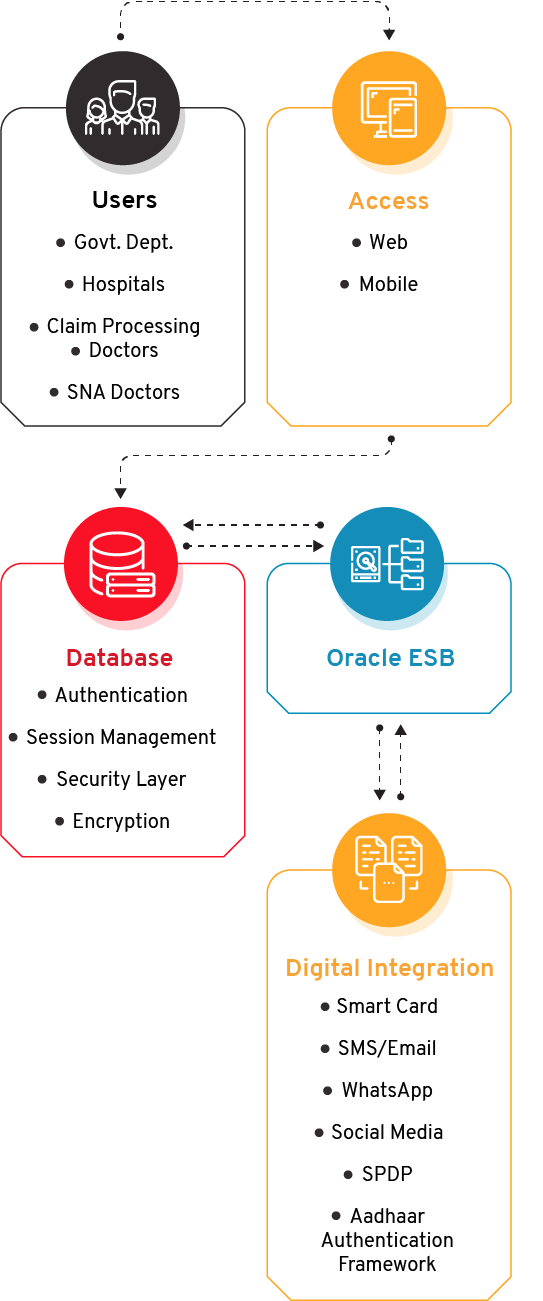
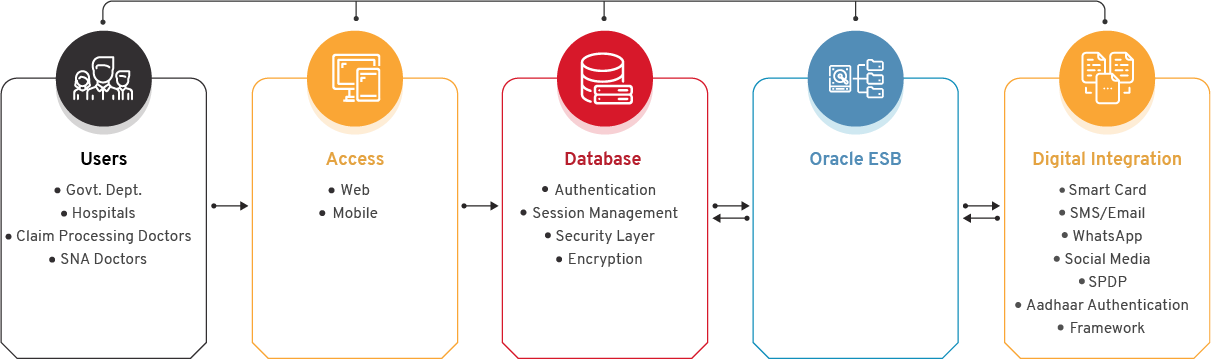
Transaction Management System: TMS captures the beneficiary information, package blocking, unblocking information, and the discharge summary.
-
Package management: Through this module addition and modification of the package can be done by the Admin user.
-
Pre- Authorization Management: This is the vital module of the system where the pre-authorization process is managed by the concerned authority. The pre-authorization requests come from the TMS module for high package costs and other pre-authorization approval.
-
Hospital Empanelment System: In this, the hospitals interested in enrolling in the BSKY scheme request for empanelment by providing various information. After approval of the request, the hospitals get empaneled.
-
Claim Management System: After the discharge of the patient, the hospital raises a claim for approval. The module helps hospitals track the status of their respective claim.
-
Mobile Application: The app is used by the State Nodal Authority (SNA) doctor for Claim approval and frontline facilitators for collecting feedback from the hospital. Hospital inspection is also done through the Mobile application.
-
Chatbot: This assistance facilitates the beneficiaries/stakeholders to instantly track the status of their query and provide answers to other FAQs.
-
Grievance: This module manages all functions required to automate the grievance/complaint management of beneficiaries and hospitals.
-
Analytical Dashboard: The system generates graphical reports for different modules to provide vital statistical information for monitoring and decision-making.
Benefits
-
Professionalism and Ethics: It integrates healthcare schemes by maintaining transparency and a sustainable environment.
-
Equity: The health policies aim to lessen the inequity and discrepancy based on caste, gender, disability, poverty, and other social exclusions. The eligible ones are the citizens who are under BPL (Below Poverty Line).
-
Affordability: The policy aims to make health services and medicines affordable. It seeks to prevent disparity in social, economic, or current health status.
-
Quality of Care: This initiative offers confidentiality in the form of safe, gender-sensitive, and convenient healthcare services in hospitals. It plans to clear corruption in both private and public healthcare systems.
-
Collaborations: It follows a multi-stakeholder approach by collaborating with health ministries and communities. Different educational institutions and non-profit agencies also partake in the initiative.